Omega 3 The Essential Fatty Acid
The Essential Fatty Acid
What is Omega 3? Omega-3 fatty acids are unique types of polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs) that are essential to human health and are of dietary importance since our bodies do not produce them.
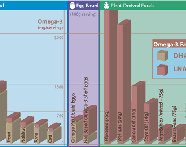
Omega 3 Content of Common Foods:
Omega-3 fatty acids are found in 3 main forms, the short-chain alpha linolenic acid (LNA) and the long-chain eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) and docosahexaenoic acid (DHA).
Recent research would suggest that EPA and DHA, or the long-chain omega-3 fatty acids are the most physiologically important to human health.
During Pregnancy: It is widely accepted that omega-3 is essential for the development of the infant brain, nerves, and visual acuity. Evidence from published research indicates that DHA specifically is an essential nutrient for early human development and functioning including neuronal performance and visual acuity. It is important that pregnant women receive sufficient levels of DHA during preconception and pregnancy to provide the necessary levels for the development of the fetus brain and retina.
Ample dietary intakes of DHA during lactation also result in higher levels of DHA being available in breast milk. Trials with infants given formula lacking DHA, compared to infants given formula with DHA, showed that providing infants with DHA early in their lives was a major factor in improving their performance on the mental development index.
Research has shown that EPA & DHA are beneficial to a woman before, during, and after pregnancy. She needs to eat foods rich in both for her own general well-being and to protect herself from cardiovascular disease, depression, inflammatory conditions, and various chronic disorders.



